The Sun

The Sun is the star at the centre of our Solar System and it's orbited by all the planets, including Earth. Without the Sun, life on Earth would not be possible as it provides heat and light for our planet.
The Sun is important to us because it is the main source of energy for life on Earth.
Nuclear reactions happen in the very hot core of the Sun when atoms of hydrogen combine. This process is called ' 'nuclear fusion' and it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
Light is important for plants to grow and the plants provide us with oxygen and lots of other things too.

Watch: Facts about the Sun
This video shares facts about the Sun and a song to help you remember them!
Narrator: Our Sun is just one of billions of stars in the Universe.
Stars are orbited by planets, who in turn, may be orbited by moons. It is truly massive.
At 1,300,000 times larger than the Earth, it is the gas fuelled fire ball that makes life possible on our planet.
As hydrogen is burned into helium at the Sun’s core, the energy created heats the solar system and produces light so strong that it should not be viewed with the naked eye…
Oh no, no, no, no, nooo… she’s back again!
Stella: Every time I look at you I put my shades on
You shine so bright, you’re a phenomenon!
We can see the moon as it reflects your light
You gas fuelled monster, you cosmic delight!
Don’t you know the Sun is a star,
Heating the Earth so I can drive my car
(With the top down)
Don’t you know the sun is a star, it doesn’t look like the others because it's not so far…
AWAAAAAAYYYYYY
Fascinating facts

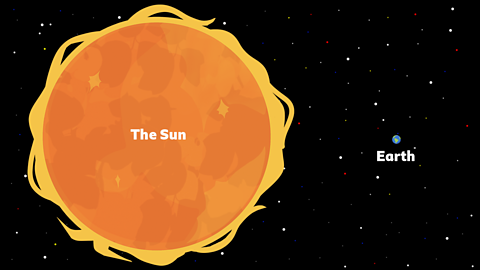
Earth is about 93 million miles from the the Sun. If we were any closer then it would be too hot for living things to survive, and if we were any further away then it would be too cold.
The Northern Lights (Aurora Borealis) are caused by charged particles from the Sun hitting gases in the Earth’s atmosphere.
The Sun is the biggest object in our Solar System.
The core of the Sun is 15 million°C.
Occasionally, dark spots freckle the face of the Sun. These are sunspots, cooler regions on the Sun caused by changes to the Sun's magnetic field.
The Sun will eventually die, but luckily for us it's not for another 5 billion years!
The Sun is made up of around 91% hydrogen gas.
The Sun is classed as a yellow dwarf star.

Slideshow: The Sun

Image caption, The Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of our solar system. It is orbited by all of the planets, including the Earth.

Image caption, Solar eclipse
The heat and light from the Sun is felt and seen on Earth. Occasionally the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun and causes a solar eclipse.

Image caption, Sunrise
Due to the Earth's rotation, the Sun always rises in the East.

Image caption, Sunset
Due to the Earth's rotation, the Sun always sets in the West.
1 of 4
Did you know?
The Sun is about 100 times wider in diameter than Earth and 1,300,000 Earths would fit inside it!

Looking at the Sun from Earth
Even though the Sun is huge when we are standing on Earth looking across the sky, the Sun seems like a tiny ball. This is because it is so far away from Earth.
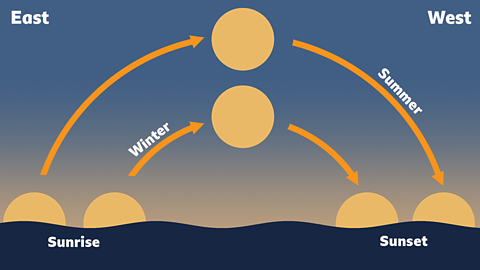
The Sun can appear to move into the sky because it isn't always in the same place when we look up, but it isn't actually the Sun moving at all… it's the Earth!
As the Earth rotates on its axis, the Sun appears to rise to the east of us, travel higher in the sky in a big arch, and then set to the west before disappearing altogether when day turns into night.
The seasons can also affect where the Sun is in the sky. The Sun appears to be much higher in the sky in the summer months, and much lower in the sky in the winter months. This is because of the way that the Earth is tilted on its axis.

Remember
You should never look at the Sun directly; it is so bright that you could damage your eyes. Scientists are able to look at the Sun by using special telescopes.

How do we use the Sun's energy?

The Sun emits (gives out) light energy, which travels to Earth and can be captured by solar panels.
The light of the Sun travels over 93 million miles to Earth in just over 8 minutes.
The Sun produces renewable energy because the Sun's energy isn't going to run out for billions of years, unlike non-renewable energy such as coal or gas.

Important words
Axis – An imaginary line running through the Earth from the North to the South Poles.
Energy – Energy is the capacity to do work. The Sun produces energy in its core through nuclear fusion when atoms of hydrogen join together.
Nuclear – Anything connected with the nucleus of an atom.
Orbited – To move in a circle around a planet or star.
Renewable – Any natural energy that we can re-use.
Solar panels – A device that can convert the Sun's light energy into electricity.
Solar System – The eight planets and their moons as well as other smaller bodies, such as asteroids and comets, which orbit the Sun.
The Sun – Our nearest star and main source of energy. The Sun is a giant ball of hot gas held together by gravity which emits huge amounts of heat and light.
Nuclear fusion - The reaction that happens in the very hot core of the Sun when atoms of hydrogen combine.

Activities
Activity 1 - Fill in the gaps
Activity 2 - Take the quiz
Activity 3 - Label the sunrise and sunset
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Earth and space
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 14

- count5 of 14
- count6 of 14
- count7 of 14

