What is the Moon?

The Moon is a large ball of rock.
It is the Earth's only natural satellite (an object that orbits a planet).
It measures 2160 miles in diameter which is about a quarter of the size of Earth.
The Moon has a rocky surface with mountains, huge craters caused by asteroid impacts, and flat plains called 'seas'.
The Moon may appear bright in the night sky, however it does not produce its own light. It reflects light from the Sun.

Watch: How we see the Moon
This demonstration shows us how we can and can't see the Moon at different times of the day.
I'm going to be the Earth, and this is the Moon.
The Moon in the sky is lit up by the Sun.
The Moon reflects the Sun's light, but the light can't go round corners, so only half of the Moon is lit up by the Sun. The other half of the Moon is dark.
The Moon orbits the Earth. As it does that, the lit-up side stays facing the Sun.
Let's look at it on its journey.
This part of its journey, me living on the Earth, I can't see any of the lit-up side. So I can't see the Moon in the sky at all. It's what we call a new moon.
As the Moon starts to make its orbit, I can suddenly see a tiny sliver of the lit-up side, so we call it a crescent moon.
I can gradually see a little bit more. That's what we call a quarter moon.
A little bit more… and that's going to carry on until the Moon is in this position. Opposite the sun, I can see all of the lit-up side. It's a full moon.
It's going to carry on around the Earth, and I can start to see less of the lit-up side and you can see a quarter moon again.
We see a crescent moon again… and once again, I can't see any of the lit-up side – it's a new moon again.
Fascinating facts

The temperatures on the Moon are extreme – they can be really hot or really cold. When the Sun's light hits the surface of the Moon, temperatures can reach a sizzling 127°C. Temperatures can plummet to a freezing -173°C when the surface of the Moon is in darkness.
The Moon possesses gravity (the force that pulls things towards the ground) just like we have on Earth. However, the Moon's gravity is weaker, which is why astronauts appear to float across its surface.
The Moon is a celestial body (a natural object found outside Earth's atmosphere) that orbits a planet. Earth only has one Moon where some planets have lots.
The Moon was formed when a celestial body the size of Mars crashed into the Earth billions of years ago.
We only ever see one side of the Moon from Earth, but this face looks different as it passes through different phases
The Moon is slowly drifting away from the Earth, approximately 3 cm a year

How does the Moon move?
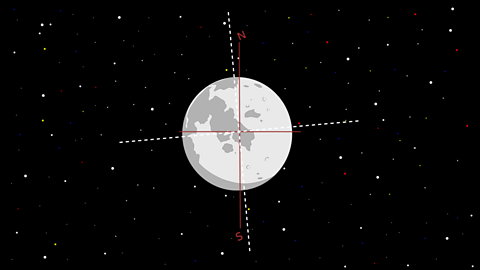
The Moon is constantly travelling around the Earth.
Like the Earth, the Moon rotates on its own axis as it orbits our planet.
It takes 27 days for the Moon to orbit our planet. In one year, the Moon can rotate around the Earth 13 times.

Slideshow: The Moon

Image caption, The Moon orbits the Earth and reflects light from the Sun which is why we see it in the night sky.

Image caption, The Moon's surface is full of deep, wide craters caused by millions of years of strikes by asteroids and meteors.

Image caption, American astronaut Neil Armstrong (1930-2012) became the first person to walk on the moon on 21 July 1969, saying the famous line "That's one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind.".

Image caption, American astronaut Gene Cernan (1934-2017) on the surface of the moon with a lunar rover, which he used to drive across the cratered dusty landscape in 1972.
1 of 4
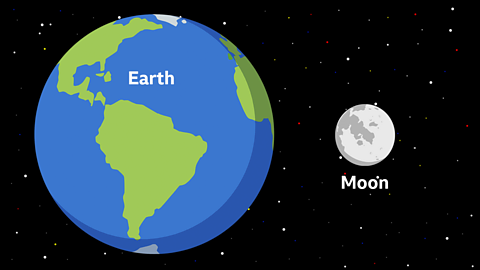
Did you know?
The diameter of the Moon is just a quarter (25%) of the size of the Earth.
The mass of the Moon is 1.2% that of the Earth.
Gravity on the lunar surface is about one-sixth of Earth's.

The Sun, Earth and Moon
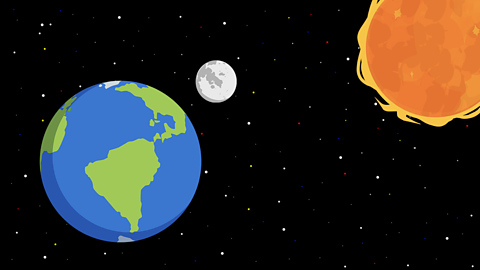
The Sun, Earth and Moon are all spherical. This means they are shaped like a ball.
The Earth is constantly travelling around the Sun and the Moon around the Earth.
When you look up at the night sky, you may have noticed how the Moon appears to change shape. This is because we can only see the part of the Moon which is illuminated by the Sun as the Moon orbits the Earth.
The Moon does not actually change shape, we just see a different view of the Moon each night.

Phases of the Moon
Sometimes, you may notice the Moon getting smaller (waning) and larger (waxing). The different shapes that we see are called the phases of the Moon.
When we see a full Moon in the sky, the Earth is in between the Sun and the Moon.
We cannot see a new Moon because the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun so we are looking towards the side of the Moon that is not illuminated.

Watch: The first person to land on the Moon
Learn about the Neil Armstrong and the first men to step onto the Moon.
FATIMA Which explorer shall we talk to today, Ollie?
OLLIE What about someone who has been to the final frontier, Fatima?
Where’s the final frontier?
Space.
Oh yeah.
Let’s talk to somebody who’s been to the Moon!
Great idea.
Holo-Lab, find the first person to set foot on the Moon.
HOLO-LAB Searching, Searching… Found. First person to set foot on the Moon: Neil Armstrong.
The Holo-lab is going back in time, before mobile phones.
Before the internet?
NEIL ARMSTRONG: Hi, I’m Neil Armstrong. In 1969, I was the first person on the Moon.
Hi Neil, we’re Fatima and Ollie and we want to ask you a few questions about the Moon landings.
Okay, sure. Nice to meet you guys. Shoot.
How did you get to the Moon, Neil?
I got to the Moon as part of the Apollo 11 mission, aboard the Saturn V rocket.
Why did you go to the Moon?
Because no one had been there before and we wanted America to be the first country to do so. The President asked NASA to design and build a rocket to take us to the Moon.
How did you get ready to go to the Moon?
I and the other two astronauts spent months training. We had to understand how to fly the rocket and land the lunar module, and how to get home again.
Was training hard work?
It was really hard work. It was great fun too. It was a real adventure into the unknown. No one had ever been to the Moon before. NASA had to develop most of the technology we needed for this trip from scratch.
Was it scary?
Between me and you, it was scary. Sitting in the huge rocket, waiting for take-off, I was super excited and… super scared. We were sitting on nearly a million litres of rocket fuel, which could explode at any moment if something went wrong. But I tried to be brave – this was it. The moment we’d been training so hard for.
NASA: Three, two, one… zero… Blast-off!
ROCKET ENGINE
Wow! Look at that!
The Earth is moving around the Sun at 70,000 miles per hour and the Moon is orbiting the Earth at 2,288 miles per hour.
The maths that allowed us to calculate the route to the Moon was so complicated, NASA had to get some of the best mathematicians in the world to figure it out. Like Katherine Johnson. She was very, very clever and got us there safely. If she’d made a single mistake in the calculations, we might not have come home at all. Our lives were in her hands.
One small step for man. One giant leap for mankind.
How did you know what to say?
We knew it was going to be a big moment and that the whole world would be watching, so we thought really hard about it.
How come you’re so bouncy?
When you’re on the Moon, gravity is just one sixth of what it is on Earth so on the Moon, I only weighed about fifteen kilograms.
What did it feel like being on the Moon?
When I was on the Moon, I looked back at the Earth where everyone I knew and loved lived, and it looked so small, like a beautiful marble.
**Wow! Thank you very much for answering all our questions, Neil Armstrong.
Thanks guys. Maybe one day, one of you will go to Mars. Whatever you do, good luck!
Mars! That would be so cool. Thanks, Neil.

Did you know?
The Moon also affects our life on Earth.
The Moon's gravitational pull makes the Earth's seas and oceans move, this is why we get a low and high tide.

Important words

Asteroid – A celestial body made of rock and metal that orbits the Sun. Asteroids often collide with other celestial bodies like the Moon.
Celestial body – Any object visible in space like a planet, an asteroid or a moon.
Crater – A circular hole on the surface of a moon or planet, caused by an impact from a meteor or asteroid.
Earth – Our planet, the third planet from the Sun.
Gravity – The force that pulls objects towards the ground.
Moon – The Moon is a huge ball of rock that orbits the Earth. Other planets also have their own moons.
Orbit – The curved path of a celestial object that moves around something which has gravity, like the Moon and the Earth.
Satellite – A celestial body orbiting a planet.
Sun – The star at the centre of our Solar System. The Sun gives off an enormous amount of light and heat.

Activities
Activity 1 – The Moon quiz
Activity 2 – Could we live on the Moon?
Think about the question: Could we live on the Moon?
Think about your answer and explain why you feel that way.
Try and think about other questions, for instance, what would a lunar base look like? How would people travel there? How would people live in the base? What would they use for food and water? How could they spend their spare time?
Carry out your own research, and use scientific evidence.

Activity 3 – Phases of the Moon
New game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space. gameNew game! Horrible Science: Stinky Space
Join Pipette on her epic mission and learn some revolting facts about space along the way.

More on Earth and space
Find out more by working through a topic
- count5 of 14
- count6 of 14
- count7 of 14

- count8 of 14

